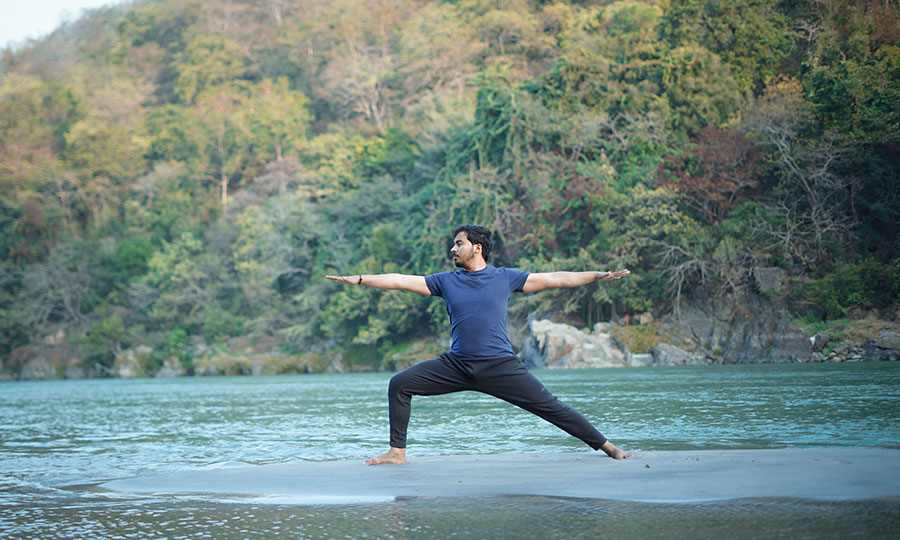
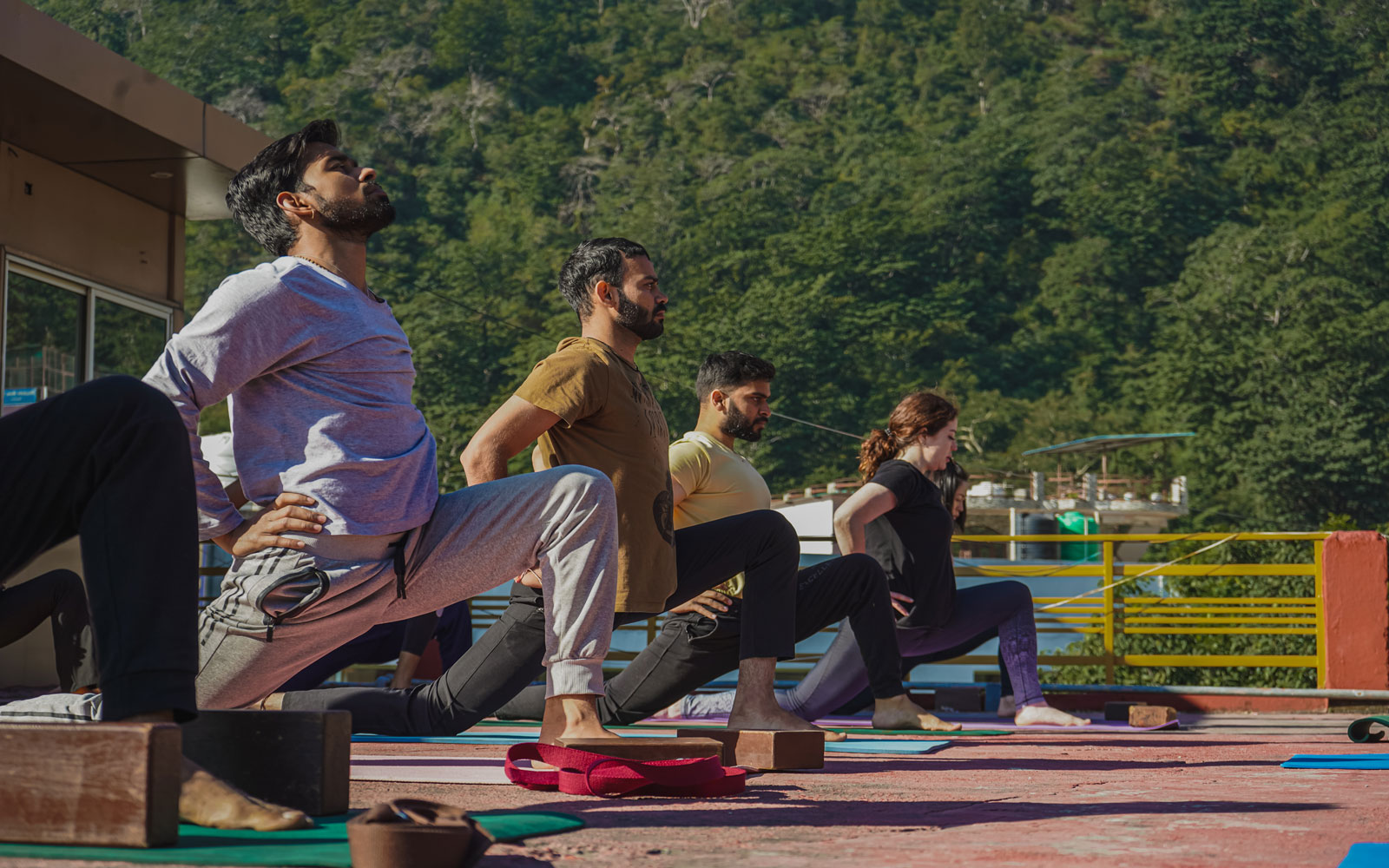
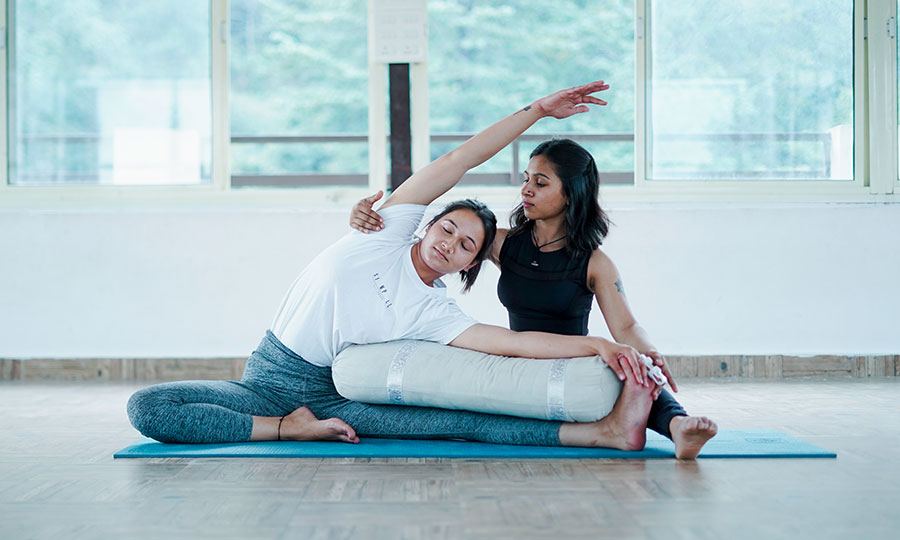
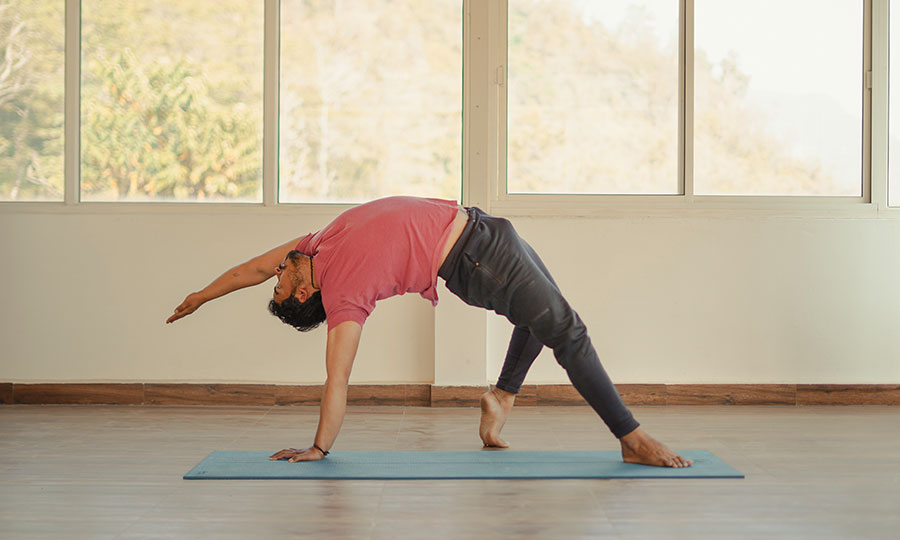
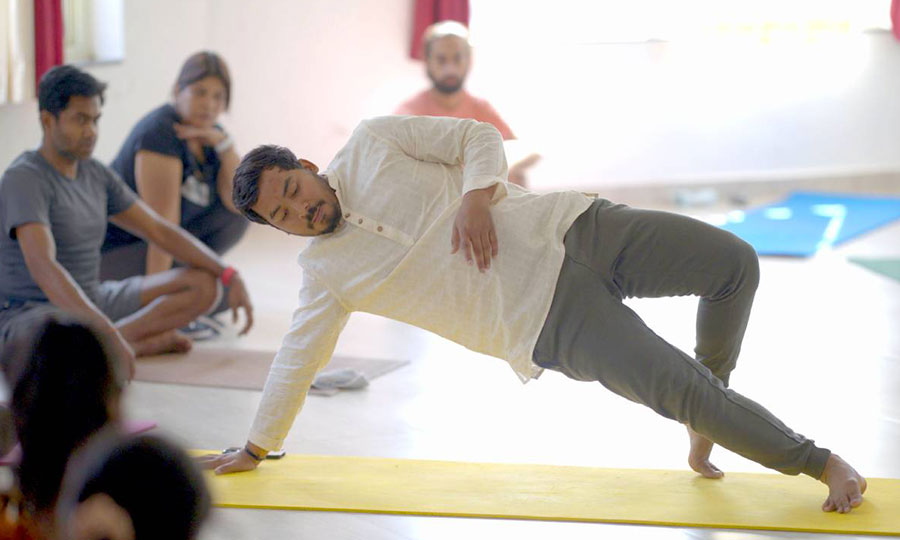
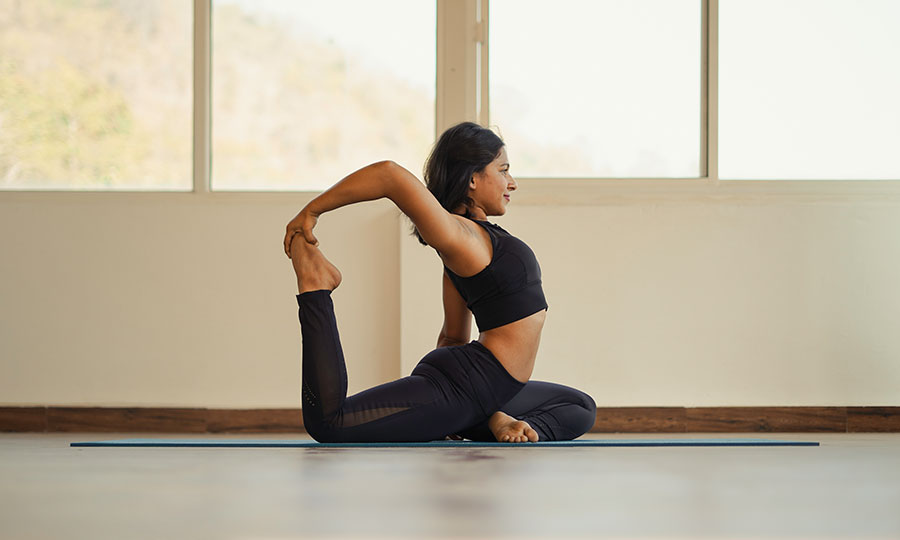
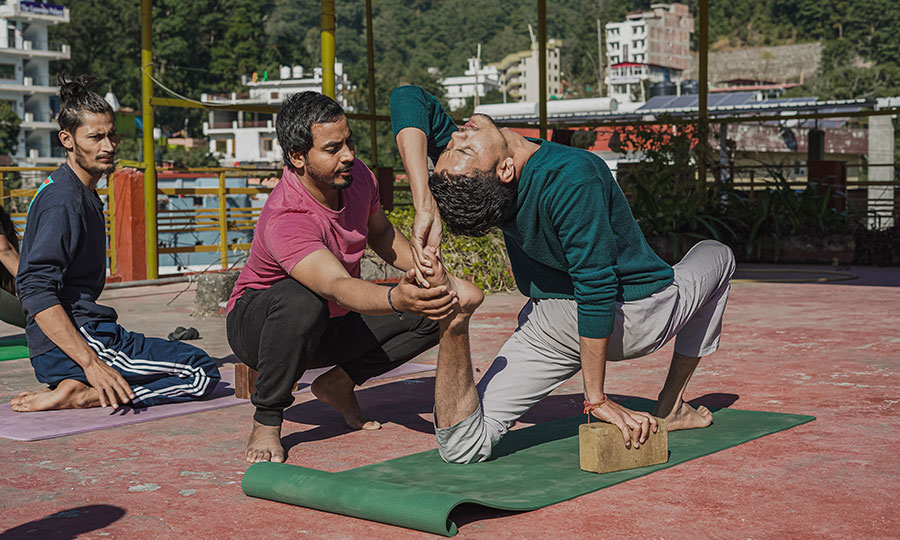
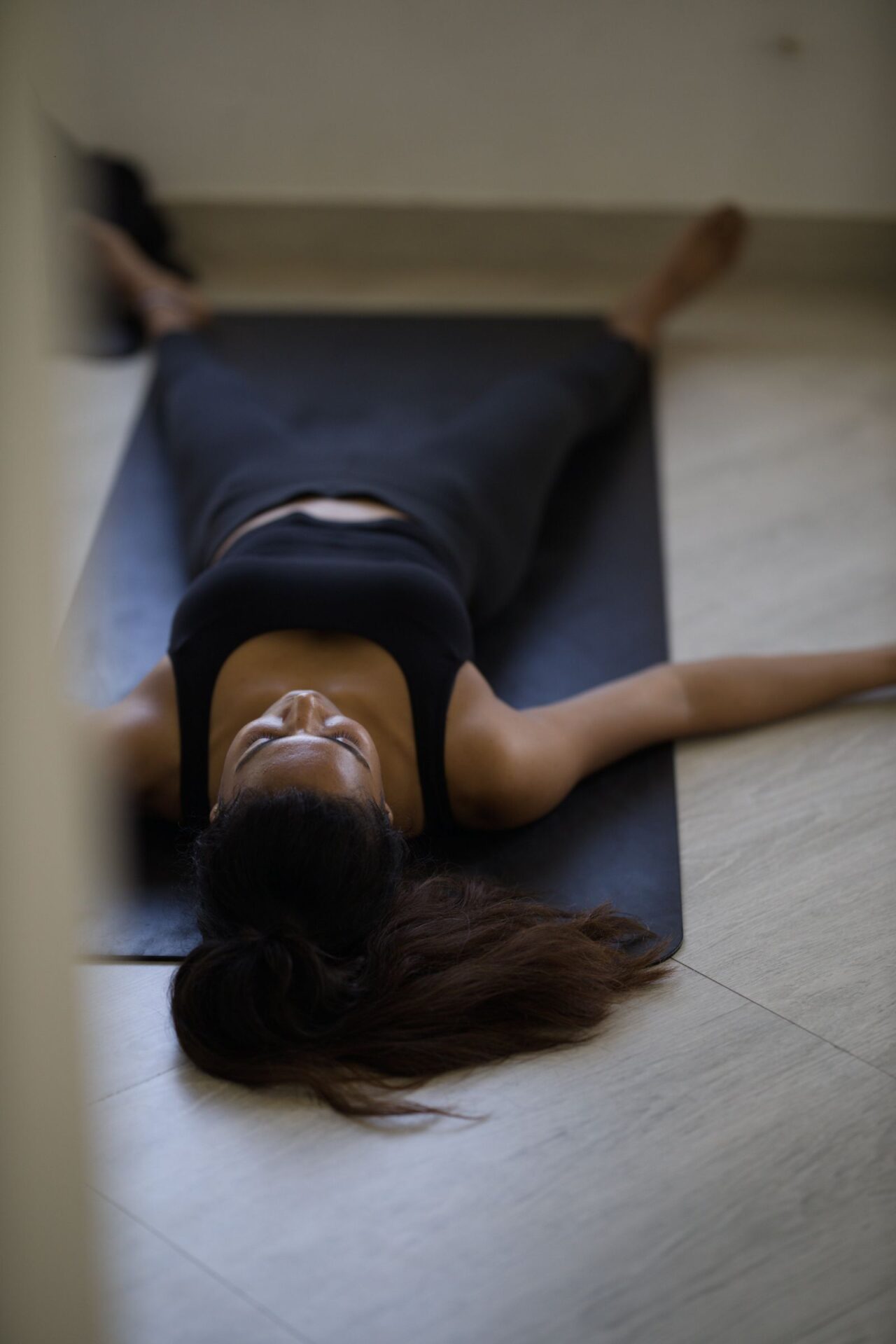
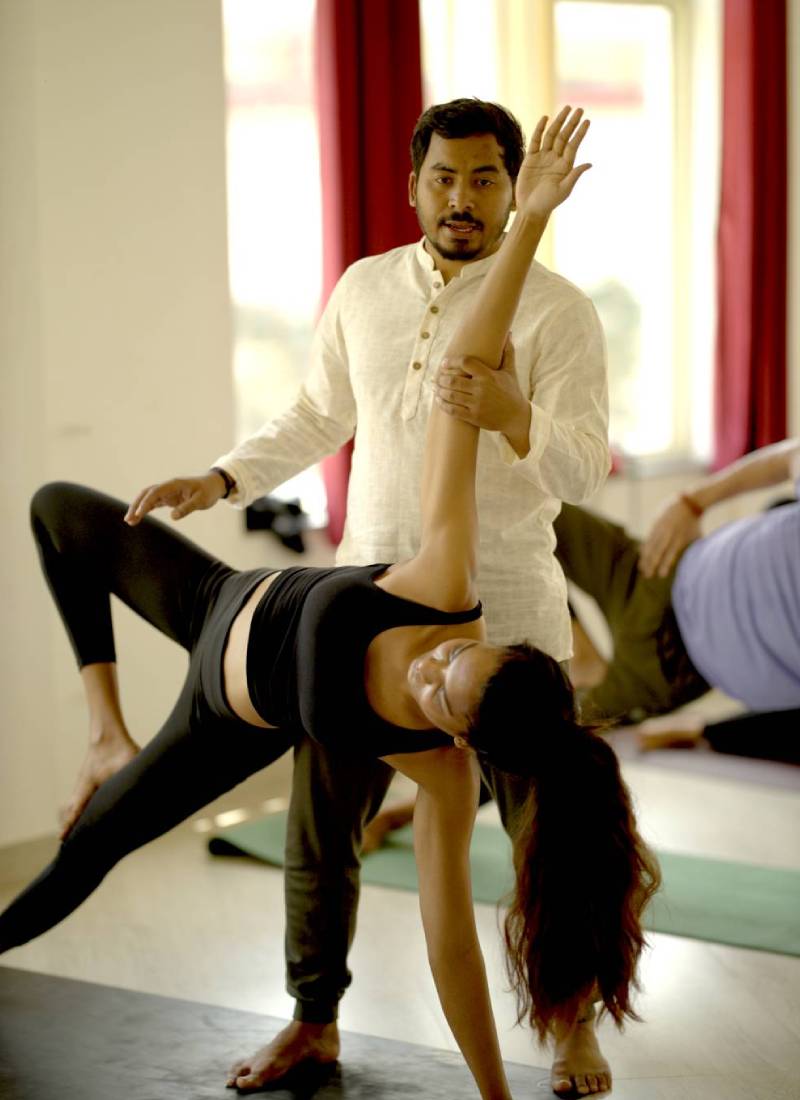
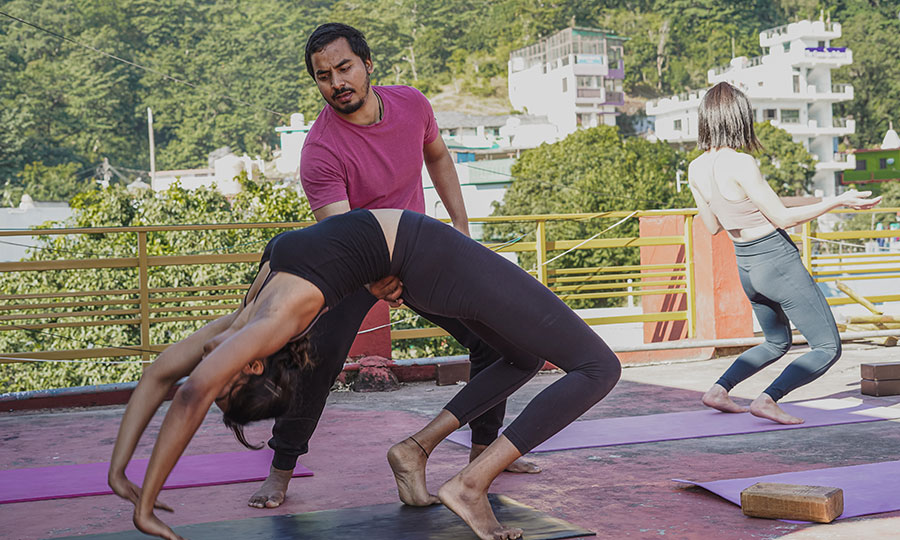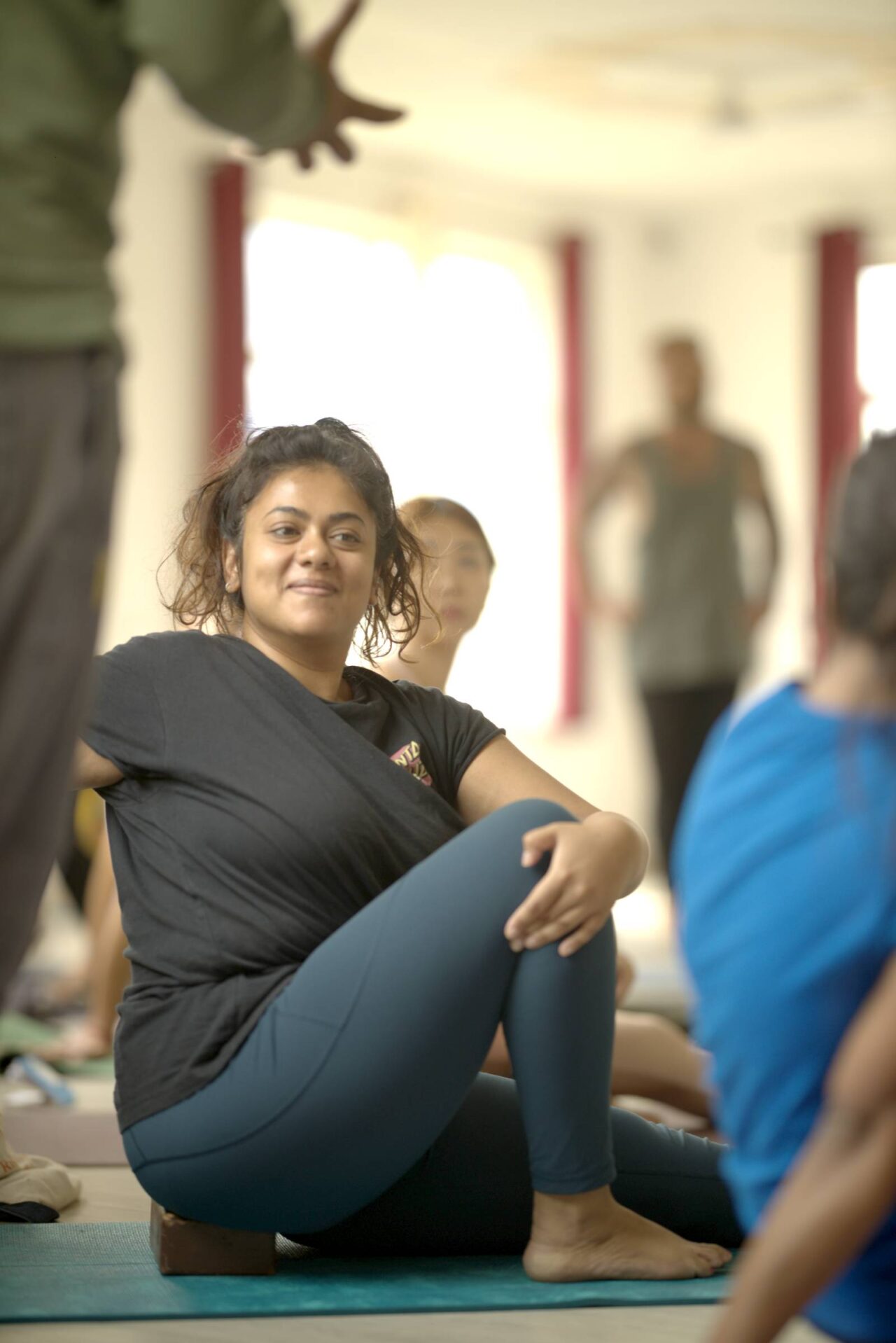Hatha Yoga
The word hatha is made up of two Sanskrit roots, ha and tha. Ha means ‘sun’and tha means ‘moon.’ This is symbolic of the twin energy forces which exist in everything. Hatha represents the forces of mind, and prana or vitality, which constitute the body and mind. The moon is the mental energy of chitta. It is the subtle force which is concerned with the mental layers. The pranic force is like the sun, dynamic and active. The two create the extremities of introversion and extroversion. It is the practice of hatha yoga which enables the fluctuations between these two energies to become harmonious and unified into one force.
- Pawanmuktasana Series 1
- Pawanmuktasana Series 2
- Pawanmuktasana Series 3
- Surya Namaskar
- Chandra Namaskar
- Tadasana
- Triyak Tadasana
- Trikonasana
- Parivirtatrikon Asana
- Utkatasana
- Virabhadrasana 1
- Virabhadrasana 2
- Ardha Chandrasana
- Vrikshasana
- Parvatasana
- Vrikshasana
- Kati Chakrasana
- Malasana
- Garudasana
- Baddha Konasana
- Rajakapotasana
- Bhujangasana
- Urdhva Mukha Svanasana
- Matsyasana
- Setu Bandhasana
- Ustrasana
- Dhanurasana
- Salabhasana
- Supta Virasana
- Virasana
- Gomukhasana
- Balasana
- Adho mukha swan asana
- Dandasana
- Ardha Matsyendrasana
- Sarpasana
- Sirsasana
- Halasana
- Sarvangasana
- UttanPadasana
- Sirsasana
Ashtanga Vinyasa
Ashtanga vinyasa yoga emphasizes certain key components, namely tristhana (“three places of action or attention”, which encompasses the physical aspects of poses, and vinyasa (which Sharath Jois defines as a system of breathing and movement).
Tristhana means the three places of attention or action: breathing system (pranayama), posture (asana), and gaze point (drishti). These are considered core concepts for ashtanga yoga practice, encompassing the three levels of purification: the body, nervous system, and the mind. They are supposed to be performed in conjunction with each other.
Each asana in ashtanga yoga is part of a set sequence, as described above. The primary aim of these poses is to enhance both the body’s strength and flexibility. It’s important to note that this style typically provides minimal alignment guidance. The recommended breathing pattern is ideally even and steady, in terms of the length of the inhalations and exhalations.
Drishti refers to the specific focal point where practitioners direct their gaze during asana practice. In Ashtanga yoga, each asana comes with a designated gazing point, known as drishti. There are nine distinct drishtis: the tip of the nose, the space between the eyebrows, the navel, the thumb, the hands, the feet, upwards, to the right, and to the left.
- Surya Namaskar A
- Surya Namaskar B
- Padangusthasana
- Padahastasana
- Utthita Trikonasana
- Parivrtta Trikonasana
- Utthita Parsvakonasana
- Parivrtta Parsvakonasana
- Prasarita Padottanasana A B C & D
- Parsvottanasana
- Utthita Hasta Padangusthasanaa A B & C
- Ardha Baddha Padmottanasana
- Utkatasana
- Virabhadrasana A & B
- Dandasana
- Paschimottanasana A, B & C
- Ardha Baddha Paschimottanasana
- Triang Mukhaikapada Paschimottanasana
- Janu Sirsasana A B & C
- Marichyasana A B C & D
- Navasana
- Bhujapidasana A & B
- Kurmasana
- Supta Kurmasana
- Garbha Pindasana
- Kukkutasana
- Baddha Konasana A & B
- Upavistha Konasana A & B
- Supta Konasana A&B
- Supta Padangusthasana
- Ubhaya Padangusthasana
- Purvottanasana
- Urdhva Mukha Paschimottanasana
- Setu Bandhasana
- Urdhva Dhanurasana
- Salamba Sarvangasana
- Halasana
- Karnapidasana
- Urdhva Padmasana
- Pindasana
- Matsyasana
- Uttana Padasana
- Sirsasana
- Urdhva Dandasana
- Yoga Mudra
- Utplutih
- Savasana
Yoga Philosophy
The difference between going to the gym and practicing yoga is the way of thinking ! Yoga, as a philosophy, provides an individual with a framework for optimizing their practices. The philosophy of yoga offers us a roadmap to follow, leading us towards a happy, healthy, and serene life. This bliss transforms into profound happiness and lasting joy. The health it bestows keeps our bodies and minds vibrant and vital. The harmony it fosters exists not only within ourselves but also with the world around us.
Through the philosophy of yoga, we find ourselves establishing physical, mental, and emotional harmony in our contemplative life experiences. Feel free to ask questions related to spirituality, meditation, or any other inquiries linked to your spiritual journey. In this course, you will explore the fundamental principles of yoga philosophy.
- Introduction To Yoga
- Concept Of Hatha Yoga
- Origin Of Yogic Practice
- Introduction To Yoga Sutra
- Yogic Discipline
- Patanjali’s Definition Of Yoga
- Types Of Vritti
- Concept Of Abhiyasa And Vairagya
- Chita-Vikchepa
- Ashtanga Yoga
- Introduction To Chakra
Pranayama
The term “prana” is a combination of two syllables, “pra” and “na.” Prana denotes constancy, it is a force in constant motion.
Prana is the vital life force, and pranayama is the method through which the body’s internal pranic reserves are expanded. Pranayama is a combination of “prana” and “ayama,” signifying “pranic capacity or length.”It is not merely breath control, but a technique through which the quantity of prana in the body is activated to a higher frequency.
Anatomy & Physiology
Yoga practice is a union of the spiritual and physical realms . Delving into the anatomy of yoga imparts valuable knowledge about physical alignment and the muscles involved in each asana.
- LEARN TO AVOID INJURY IN YOUR PRACTICE OR THAT OF YOUR STUDENTS
- BECOME PROFICIENT IN YOUR KNOWLEDGE OF THE ANATOMY OF THE BODY
- UNDERSTAND THE EFFECTS OF EXERCISE ON ALL THE SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
- EXPERT INSTRUCTORS – HIGHLY ACCLAIMED
- GAIN CONTINUING EDUCATION POINTS
Meditation
Meditation is a practice that involves training the mind to focus and become more aware of the present moment. It is a mental exercise that is often used for relaxation, stress reduction, and spiritual growth.
Meditation can take many forms, but most techniques involve sitting or lying down in a comfortable position and focusing your attention on a specific object, thought, or sensation. Some common meditation techniques include mindfulness meditation, guided visualization, loving-kindness meditation, and transcendental meditation.
Regular meditation practice offers numerous advantages, such as alleviating stress and anxiety, enhancing concentration and focus, elevating self-awareness and emotional control, and promoting overall physical and mental well-being. Through consistent practice, meditation can help you cultivate a sense of inner calm and stillness, empowering you to navigate life’s challenges with greater ease and grace.